Title: Pneumonia: Signs, Symptoms, Causes, Risk Factors, Diagnosis, Prevention, Diet, Lifestyle, and Homoeopathic Treatment
Introduction:
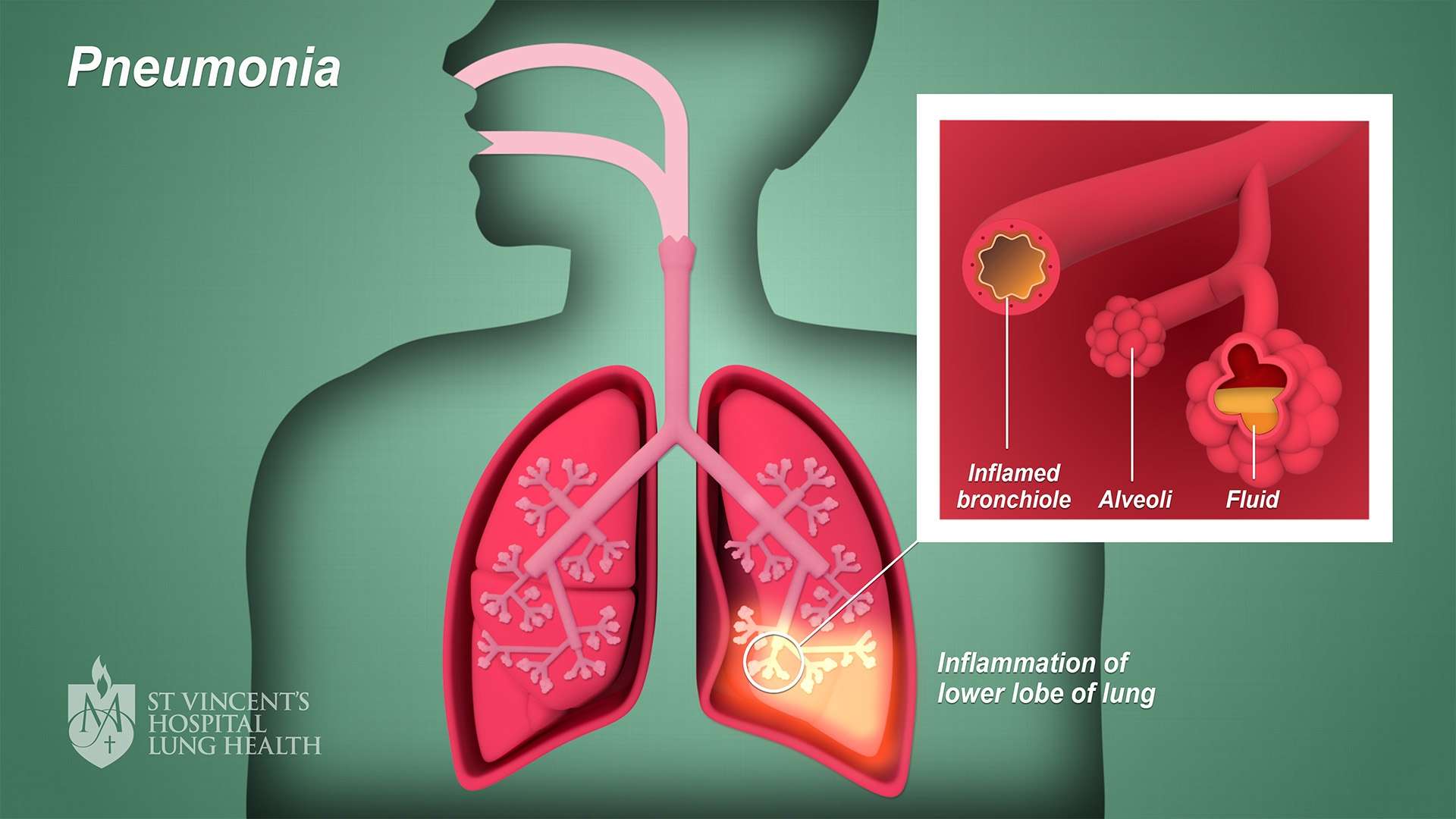
Pneumonia is a respiratory infection that affects the lungs, causing inflammation and leading to various symptoms. Understanding the signs, symptoms, causes, risk factors, diagnosis methods, prevention strategies, diet and lifestyle considerations, and the potential role of homoeopathic treatment is crucial for effectively managing pneumonia. In this blog post, we will explore the key aspects of pneumonia and its holistic approach to treatment.
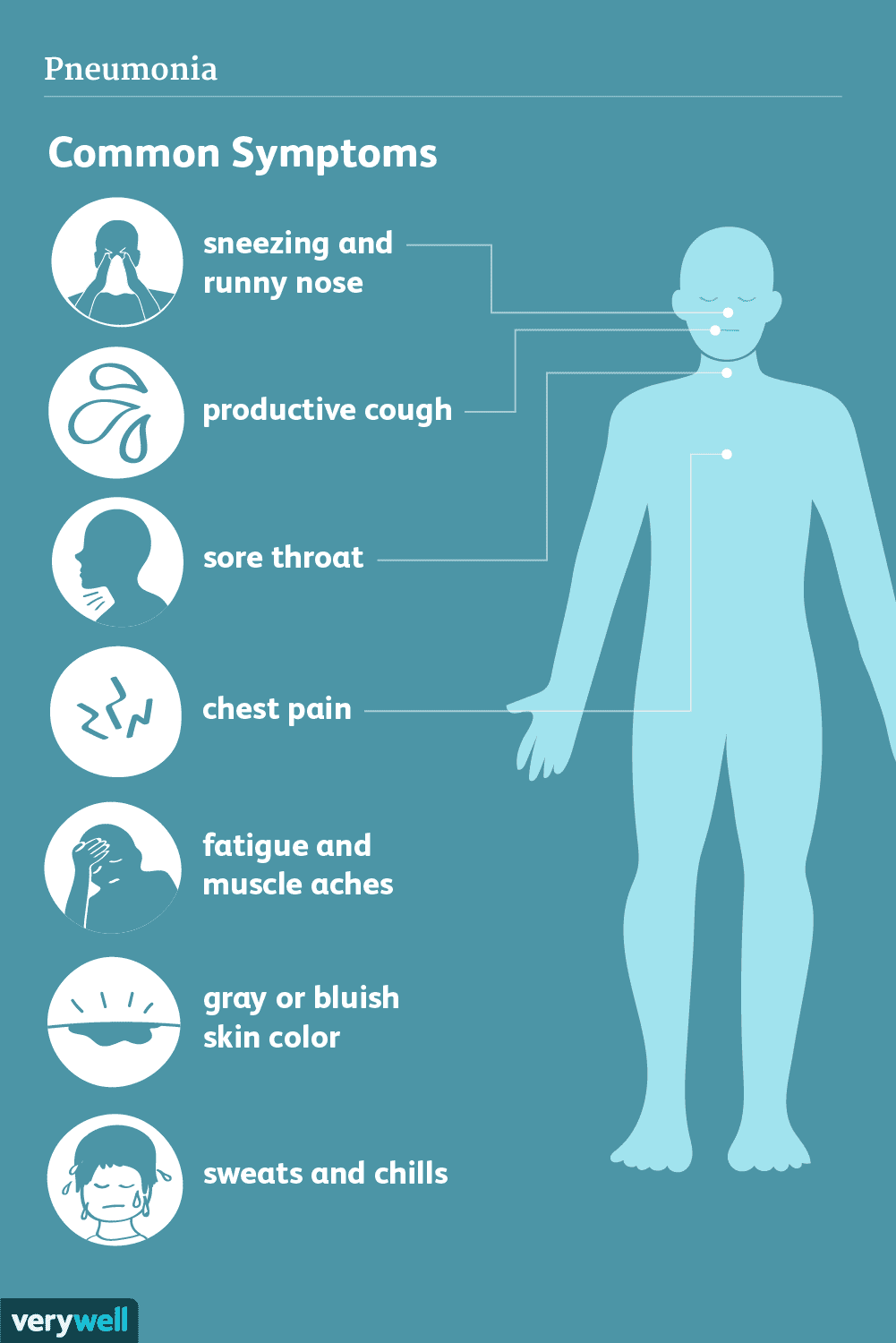
Signs and Symptoms of Pneumonia:
1. Cough: May produce phlegm or pus, which can be green, yellow, or bloody.
2. Fever: High body temperature, often accompanied by chills and sweating.
3. Shortness of breath: Difficulty breathing or rapid, shallow breathing.
4. Chest pain: Sharp or stabbing pain that worsens with deep breathing or coughing.
5. Fatigue: Feeling tired and weak.
6. Confusion (especially in older adults): Disorientation or changes in mental awareness.
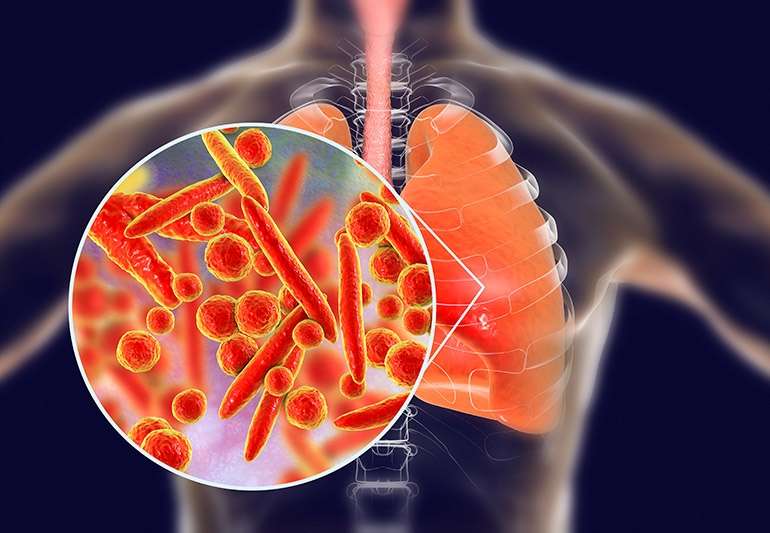
Common Causes of Pneumonia:
1. Bacterial infection: Streptococcus pneumoniae is the most common bacterial cause of pneumonia.
2. Viral infection: Influenza viruses, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and rhinoviruses can lead to viral pneumonia.
3. Fungal infection: Certain fungi, such as Pneumocystis jirovecii, can cause pneumonia, especially in individuals with weakened immune systems.
Risk Factors for Pneumonia:
1. Age: Young children and older adults are more susceptible to pneumonia.
2. Weakened immune system: Conditions like HIV/AIDS, cancer, or organ transplantation weaken the immune system, making individuals more vulnerable to infections.
3. Chronic lung diseases: Asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), or bronchiectasis increase the risk of developing pneumonia.
4. Smoking: Smoking damages the lungs and impairs the body's ability to fight infections.
5. Hospitalization: Being in a healthcare setting increases the risk of acquiring pneumonia.
6. Living conditions: Crowded living conditions or exposure to certain environmental pollutants can contribute to pneumonia.
Diagnosis of Pneumonia:
1. Physical examination: The healthcare provider will listen to the lungs with a stethoscope to assess for abnormal lung sounds.
2. Chest X-ray: This imaging test helps identify areas of lung inflammation or consolidation.
3. Blood tests: These can indicate the presence of infection and determine the type of organism causing pneumonia.
4. Sputum culture: Collecting a sample of coughed-up phlegm to identify the specific pathogen causing pneumonia.
Prevention Strategies for Pneumonia:
1. Vaccination: Receive recommended vaccines, such as the pneumococcal vaccine and influenza vaccine, to reduce the risk of pneumonia.
2. Hand hygiene: Wash hands frequently with soap and water or use alcohol-based hand sanitizers.
3. Avoid smoking: Quit smoking and avoid secondhand smoke exposure to protect the lungs.
4. Respiratory hygiene: Cover the mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing, preferably with a tissue or the elbow.
5. Stay healthy: Maintain a strong immune system through regular exercise, a balanced diet, adequate sleep, and managing stress.
Diet and Lifestyle Considerations:
1. Balanced diet: Consume a variety of nutrient-rich foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats to support overall health and immune function.
2. Hydration: Drink plenty of fluids to stay hydrated and thin mucus secretions.
3. Rest and sleep: Allow the body to recover by getting enough rest and sleep.
4. Avoid exposure: Minimize contact with individuals who have respiratory infections to reduce the risk of contracting pneumonia.
Homoeopathic Treatment for Pneumonia:
Homoeopathic treatment for pneumonia aims to address the underlying causes, strengthen the immune system, and promote respiratory health. Some commonly used homoeopathic remedies for pneumonia include:
1. Bryonia alba: Indicated for pneumonia with sharp chest pain worsened by movement, dry cough, and difficulty breathing.
2. Antimonium tartaricum: Useful for pneumonia with rattling cough, excessive mucus, and difficulty expectorating.
3. Phosphorus: Recommended for pneumonia with a dry or loose cough, weakness, and shortness of breath.
It is important to consult a qualified homoeopathic practitioner for an accurate diagnosis and individualized treatment plan based on your specific symptoms and overall health.
Conclusion:
Pneumonia is a respiratory infection that requires prompt attention and management. By understanding the signs, symptoms, causes, risk factors, diagnosis methods, prevention strategies, diet and lifestyle considerations, and considering homoeopathic treatment as a complementary approach, individuals can effectively manage pneumonia and support their recovery. Always consult healthcare professionals for an accurate diagnosis and to create a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to your specific needs.
Leave a Message