Title: Female Infertility: Signs, Symptoms, Causes, Risk Factors, Diagnosis, Prevention, Diet, Lifestyle, and Homoeopathic Treatment
Introduction:
Infertility is a distressing condition that affects many couples worldwide. When it comes to female infertility, understanding the signs, symptoms, causes, risk factors, diagnosis methods, prevention strategies, the role of diet and lifestyle, and exploring the potential of homoeopathic treatment is crucial. In this blog post, we will delve into the key aspects of female infertility and the holistic approach of homoeopathy in its management.
Signs and Symptoms of Female Infertility:
1. Irregular menstrual cycles: Abnormal or inconsistent menstrual periods.
2. Hormonal imbalances: Symptoms like excessive hair growth (hirsutism), acne, or weight gain.
3. Painful periods: Severe menstrual cramps (dysmenorrhea) that interfere with daily activities.
4. Pelvic pain: Chronic or intermittent pain in the pelvic region.
5. Abnormal or absent ovulation: Difficulty in conceiving or anovulation (lack of ovulation).
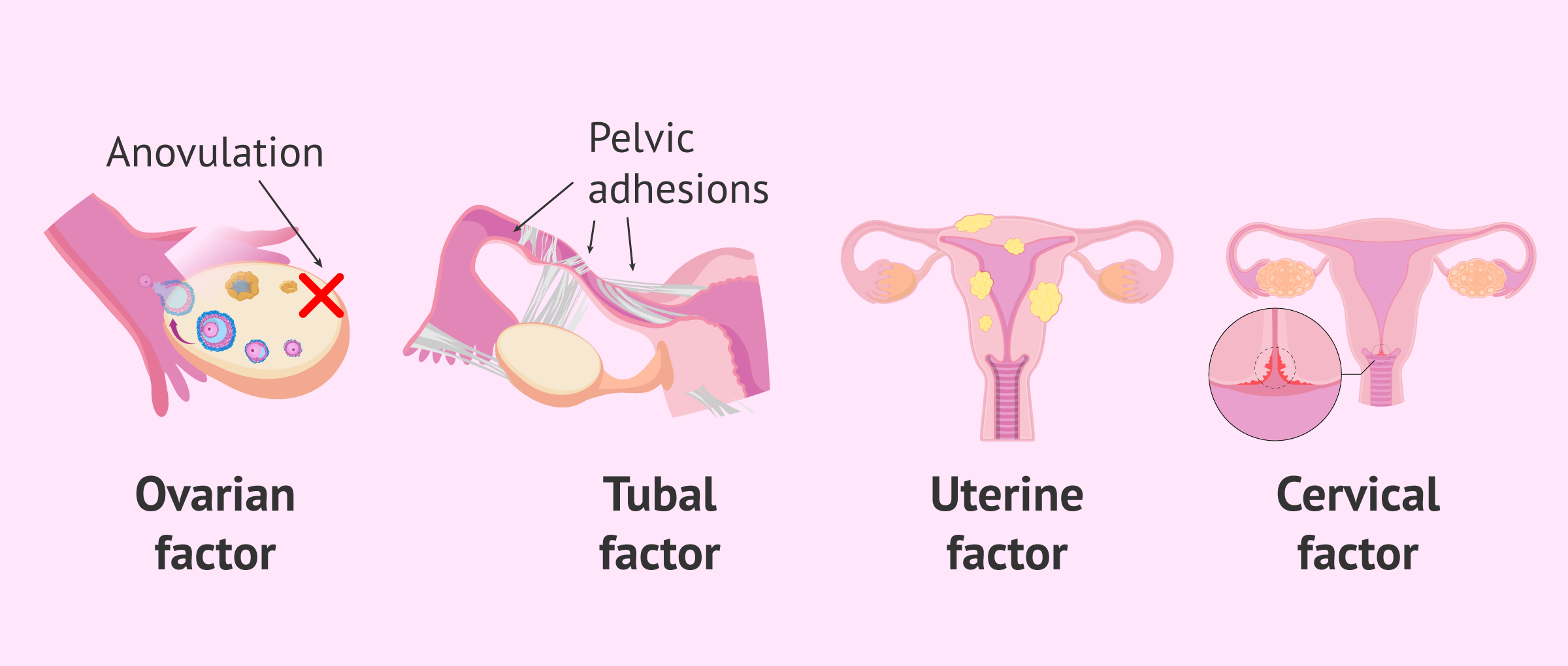
Common Causes of Female Infertility:
1. Ovulation disorders: Conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or hormonal imbalances affecting regular ovulation.
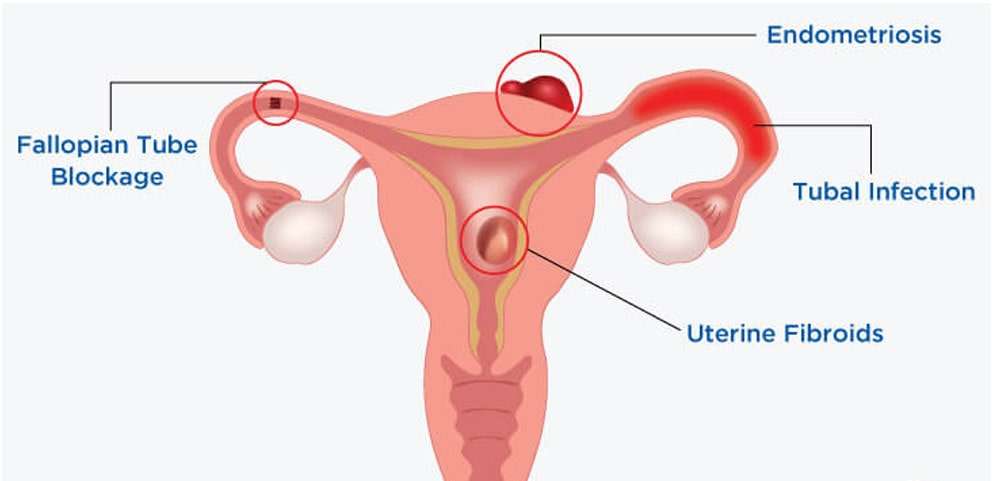
2. Structural abnormalities: Issues with the fallopian tubes, uterus, or cervix, including blocked fallopian tubes or uterine fibroids.
3. Endometriosis: The growth of endometrial tissue outside the uterus.
4. Age-related factors: Decreased ovarian reserve and diminished fertility as women age.
5. Medical conditions and treatments: Certain medical conditions, such as thyroid disorders or cancer treatments like chemotherapy or radiation, can affect fertility.
Risk Factors for Female Infertility:
1. Age: Fertility declines with age, particularly after the age of 35.
2. Smoking: Cigarette smoking can adversely affect fertility.
3. Obesity: Being overweight or obese can impact fertility and increase the risk of ovulation disorders.
4. Stress: High levels of stress can interfere with reproductive hormones and ovulation.
5. Chronic illnesses: Conditions like diabetes or autoimmune disorders can affect fertility.
Diagnosis of Female Infertility:
1. Medical history and physical examination: Evaluating menstrual history, symptoms, and potential risk factors.
2. Hormone testing: Assessing hormone levels to identify ovulation disorders or hormonal imbalances.
3. Ovulation tracking: Monitoring basal body temperature or using ovulation predictor kits to determine if ovulation is occurring.
4. Imaging tests: Ultrasound or hysterosalpingography to evaluate the structure of the reproductive organs.
5. Laparoscopy: A minimally invasive procedure to examine the pelvic organs, particularly for suspected endometriosis.
Prevention, Diet, and Lifestyle Considerations:
1. Maintain a healthy weight: Aim for a healthy BMI through regular exercise and a balanced diet.
2. Quit smoking: Smoking can negatively impact fertility, so it's essential to quit.
3. Manage stress: Incorporate stress management techniques such as yoga, meditation, or counseling into your routine.
4. Limit alcohol and caffeine: Excessive alcohol and caffeine consumption may affect fertility.
5. Practice safe sex: Prevent sexually transmitted infections (STIs) that can lead to reproductive complications.
Dietary Recommendations:
1. Balanced diet: Consume a variety of nutrient-rich foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
2. Antioxidant-rich foods: Include foods like berries, citrus fruits, nuts, and seeds, which are rich in antioxidants that may support reproductive health.
3. Iron-rich foods: Ensure adequate intake of iron-rich foods like leafy greens, beans, and fortified cereals to support healthy blood levels.
Homoeopathic Treatment for Female Infertility:
Homoeopathic treatment for female infertility aims to address the underlying causes, promote hormonal balance, and enhance reproductive health. Some commonly used homoeopathic remedies for female infertility include:
1. Sepia: Indicated for irregular periods, hormonal imbalances, and diminished sexual desire.
2. Pulsatilla: Useful for hormonal imbalances with delayed or absent periods, emotional sensitivity, and changeable moods.
3. Lycopodium: Recommended for infertility due to hormonal imbalances, polycystic ovaries, or age-related factors.
It is important to consult a qualified homoeopathic practitioner for an accurate diagnosis, individualized treatment plan, and monitoring of progress.
Conclusion:
Female infertility can be a challenging condition, but with proper understanding of its signs, causes, risk factors, diagnosis methods, prevention strategies, and the potential of homoeopathic treatment, it is possible to manage and improve reproductive health. Remember to consult healthcare professionals for an accurate diagnosis and to create a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to your specific needs. Homoeopathy offers a holistic approach that considers the individual as a whole, aiming to address the underlying causes and promote overall well-being.

Leave a Message