Title: Liver Cirrhosis: Understanding Signs, Symptoms, Causes, Risk Factors, Diagnosis, Prevention, Diet, Lifestyle, and Homoeopathic Treatment
Introduction:
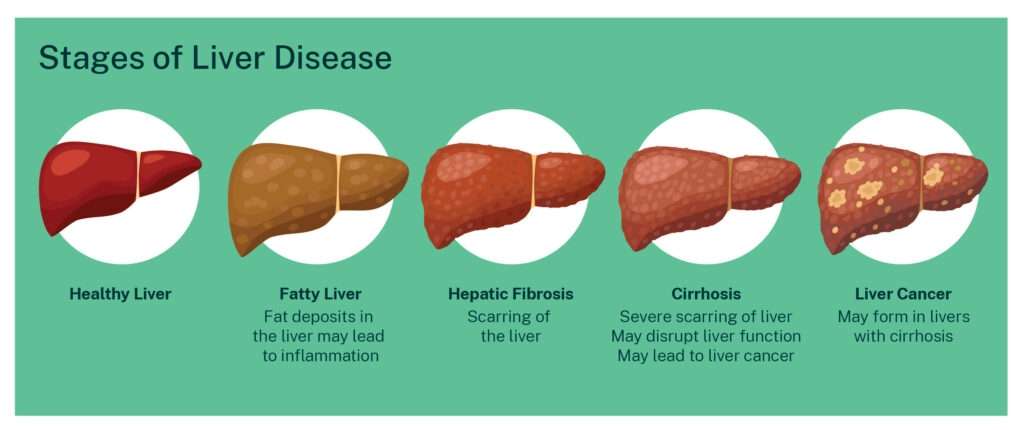
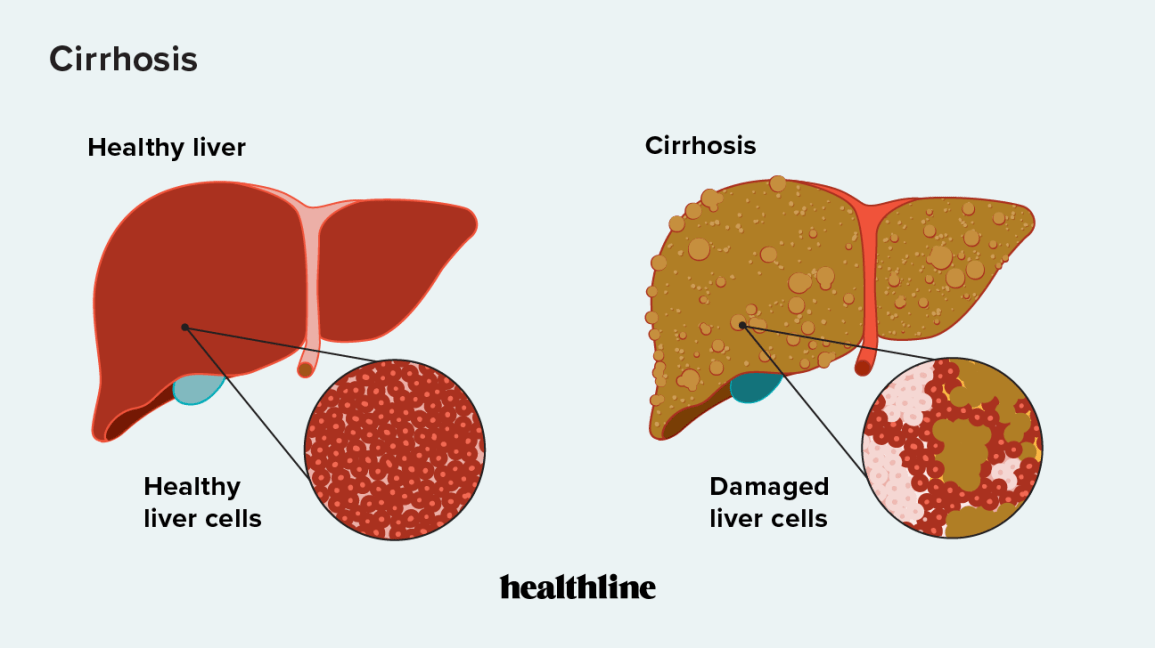
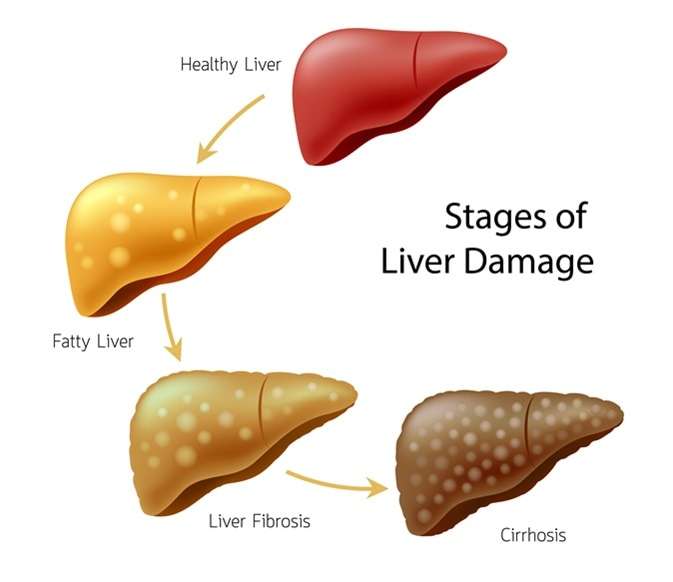
Liver cirrhosis is a progressive liver disease characterized by the scarring and damage of liver tissue. It can have significant impacts on a person's health and well-being. Understanding the signs, symptoms, causes, risk factors, diagnosis methods, prevention strategies, diet and lifestyle considerations, and the potential role of homoeopathic treatment is crucial for effectively managing liver cirrhosis. In this blog post, we will explore the key aspects of liver cirrhosis and its holistic approach to treatment.
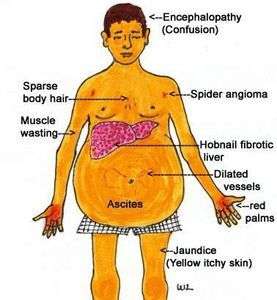
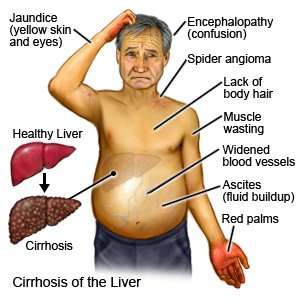
Signs and Symptoms of Liver Cirrhosis:
1. Fatigue and weakness: Feeling tired and lacking energy.
2. Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin and eyes.
3. Abdominal swelling: Accumulation of fluid in the abdomen (ascites).
4. Easy bruising and bleeding: Decreased production of clotting factors.
5. Itchy skin: Buildup of bile products in the bloodstream.
6. Loss of appetite and weight loss: Reduced desire to eat and unintentional weight loss.
7. Mental confusion: Impaired brain function (hepatic encephalopathy).
Common Causes of Liver Cirrhosis:
1. Chronic alcohol abuse: Excessive and prolonged alcohol consumption.
2. Chronic viral hepatitis: Hepatitis B or C infections.
3. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): Accumulation of fat in the liver due to obesity, diabetes, or metabolic syndrome.
4. Autoimmune hepatitis: The immune system mistakenly attacks liver cells.
5. Genetic disorders: Inherited conditions such as hemochromatosis or Wilson's disease.
Risk Factors for Liver Cirrhosis:
1. Alcohol consumption: Excessive and prolonged alcohol abuse is a significant risk factor.
2. Chronic viral hepatitis: Long-term infection with hepatitis B or C.
3. Obesity and metabolic syndrome: Conditions that can lead to NAFLD and subsequent cirrhosis.
4. Family history: Certain genetic liver disorders can increase the risk.
5. Diabetes: Poorly controlled diabetes can contribute to the development of liver disease.
Diagnosis of Liver Cirrhosis:
Liver cirrhosis can be diagnosed through various methods, including:
1. Medical history and physical examination: Discussing symptoms, risk factors, and medical history with a healthcare professional.
2. Blood tests: Assessing liver function, checking for viral infections, and measuring certain enzymes and proteins.
3. Imaging tests: Ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI to evaluate liver structure and identify signs of cirrhosis.
4. Liver biopsy: Removal of a small sample of liver tissue for microscopic examination.
Prevention Strategies, Diet, and Lifestyle Considerations:
1. Limit alcohol consumption: Practice moderate or abstinence from alcohol, especially if you have a history of liver disease.
2. Vaccination: Get vaccinated against hepatitis A and B viruses to reduce the risk of viral hepatitis.
3. Practice safe sex and avoid sharing needles: Prevent transmission of hepatitis B and C viruses.
4. Maintain a healthy weight: Follow a balanced diet, engage in regular exercise, and manage conditions like obesity and diabetes.
5. Avoid exposure to toxins: Limit contact with chemicals and toxins that can harm the liver.
Diet and Lifestyle Considerations:
1. Balanced diet: Consume a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
2. Limit sodium intake: Reduce salt consumption to manage fluid retention and swelling.
3. Hydration: Drink an adequate amount of water to maintain liver health.
4. Regular exercise: Engage in physical activity to support overall liver health and promote weight management.
5. Quit smoking: Smoking can worsen liver disease and
increase the risk of complications.
Homoeopathic Treatment for Liver Cirrhosis:
Homoeopathic treatment for liver cirrhosis aims to address the underlying causes, alleviate symptoms, and support liver function. Some commonly used homoeopathic remedies for liver cirrhosis include:
1. Carduus marianus: Indicated for liver cirrhosis with pain in the right upper abdomen, jaundice, and digestive disturbances.
2. Chelidonium majus: Useful for liver cirrhosis with enlargement of the liver, jaundice, and right-sided abdominal pain.
3. Lycopodium clavatum: Recommended for liver cirrhosis with bloating, flatulence, and digestive disorders.
It is essential to consult a qualified homoeopathic practitioner for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan based on your specific symptoms and overall health.
Conclusion:
Liver cirrhosis is a complex condition that requires comprehensive management. By understanding the signs, symptoms, causes, risk factors, diagnosis methods, prevention strategies, diet and lifestyle considerations, and exploring homoeopathic treatment as a complementary approach, individuals can effectively manage liver cirrhosis and improve their overall well-being. Always consult healthcare professionals for an accurate diagnosis and to create a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to your specific needs.
Leave a Message