Title: Nephritis: Understanding Signs, Symptoms, Causes, Risk Factors, Diagnosis, Prevention, Diet, Lifestyle, and Homoeopathic Treatment
Introduction:
Nephritis refers to inflammation of the kidneys, which can lead to kidney damage and impaired kidney function. Understanding the signs, symptoms, causes, risk factors, diagnosis methods, prevention strategies, diet and lifestyle considerations, and the potential role of homoeopathic treatment is crucial for effectively managing nephritis. In this blog post, we will explore the key aspects of nephritis and its holistic approach to treatment.
Signs and Symptoms of Nephritis:
1. Blood in the urine (hematuria): Pink, red, or brown-colored urine.
2. Foamy urine: Increased protein levels in the urine can cause it to appear foamy.
3. Edema: Swelling in the hands, feet, ankles, or face due to fluid retention.
4. High blood pressure: Elevated blood pressure levels.
5. Fatigue and weakness: Feeling tired and lacking energy.
6. Decreased urine output: Reduced frequency and volume of urination.
Common Causes of Nephritis:
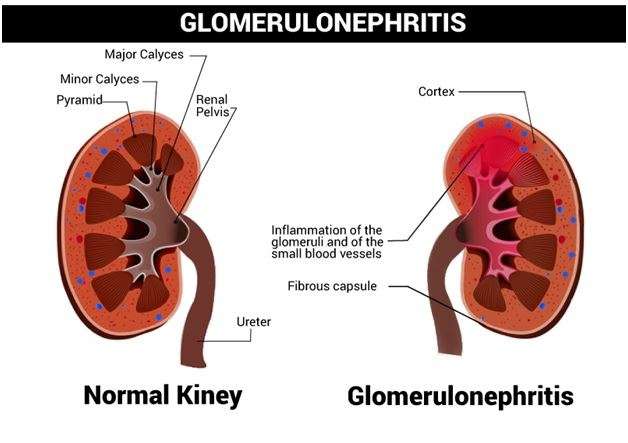
1. Glomerulonephritis: Inflammation of the glomeruli, the filtering units of the kidneys, often caused by immune system disorders or infections.
2. Interstitial nephritis: Inflammation of the kidney tubules and interstitium, often due to medications, infections, or autoimmune diseases.
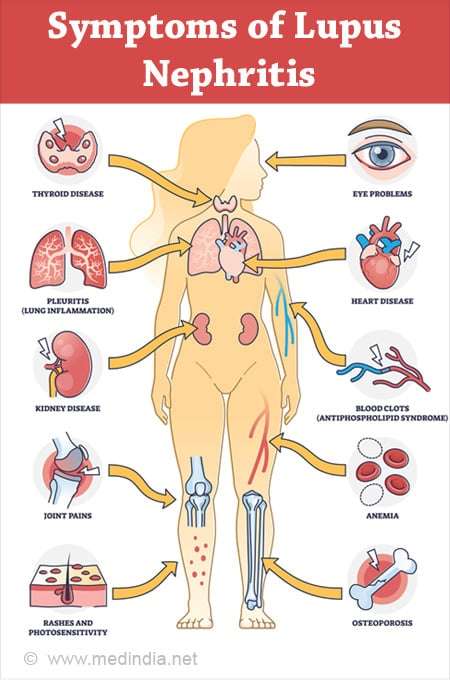
3. Lupus nephritis: Kidney inflammation as a result of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), an autoimmune disease.
4. Pyelonephritis: Kidney infection usually caused by bacteria ascending from the bladder or urinary tract.
Risk Factors for Nephritis:
1. Age and gender: Certain forms of nephritis, such as lupus nephritis, are more common in females and often occur in younger individuals.
2. Autoimmune diseases: Conditions like systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), rheumatoid arthritis, and vasculitis increase the risk of nephritis.
3. Infections: Bacterial or viral infections, especially those affecting the urinary tract or respiratory system, can contribute to nephritis.
4. Medications: Certain medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), antibiotics, and diuretics, may increase the risk of nephritis.
5. Family history: A family history of kidney disease or autoimmune disorders may predispose individuals to nephritis.
Diagnosis of Nephritis:
Nephritis can be diagnosed through various methods, including:
1. Urine tests: Analysis of urine for the presence of blood, protein, and other abnormalities.
2. Blood tests: Measurement of kidney function, including blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine levels.
3. Imaging tests: Ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI to visualize the kidneys and detect any abnormalities.
4. Kidney biopsy: Collection of a small sample of kidney tissue for examination under a microscope.
Prevention Strategies, Diet, and Lifestyle Considerations:
1. Manage underlying conditions: Proper management of autoimmune diseases, infections, and other underlying conditions can help prevent nephritis.
2. Stay hydrated: Maintain adequate fluid intake to support kidney function and prevent dehydration.
3. Follow medication instructions: Take medications as prescribed and discuss potential side effects with your healthcare provider.
4. Maintain a healthy lifestyle: Exercise regularly, manage stress levels, and avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
Dietary Recommendations for Nephritis:
1. Reduce salt intake: Limiting sodium helps manage fluid retention and control blood pressure.
2. Monitor protein intake: Consult with a healthcare provider or dietitian to determine the appropriate amount of protein for your condition.
3. Eat a balanced diet: Include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats in your meals.
4. Limit potassium and phosphorus: If advised by your healthcare provider, limit high-potassium and high-phosphorus foods, such as bananas, oranges, dairy products, and processed foods.
Homoeopathic Treatment for Nephritis:
Homoeopathy offers a holistic approach to treating nephritis by addressing the underlying causes, reducing inflammation, and supporting kidney function. Some commonly used homoeopathic remedies for nephritis include:
1. Apis mellifica: Indicated for nephritis with edema, scanty urine, and burning sensations.
2. Cantharis: Useful for nephritis with intense burning and cutting pain during urination.
3. Arsenicum album: Recommended for nephritis with weakness, restlessness, and anxiety.
It is important to consult a qualified homoeopathic practitioner for an accurate diagnosis and individualized treatment plan based on your specific symptoms and overall health.
Conclusion:
Nephritis requires careful management to preserve kidney function and overall well-being. By understanding the signs, symptoms, causes, risk factors, prevention strategies, diet and lifestyle considerations, and considering homoeopathic treatment as a complementary approach, individuals can effectively manage nephritis. Remember to consult healthcare professionals for an accurate diagnosis and to create a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to your specific needs.
Leave a Message