Title: Mouth Cancer: Signs, Symptoms, Causes, Risk Factors, Diagnosis, Prevention, Diet, Lifestyle, and Homoeopathic Medicine
Introduction:
Mouth cancer, also known as oral cancer, refers to the abnormal growth of cells in the oral cavity. Early detection and understanding the signs, symptoms, causes, risk factors, diagnosis methods, prevention strategies, diet and lifestyle considerations, and the potential role of homoeopathic medicine are crucial for effectively managing this condition. In this blog post, we will explore the key aspects of mouth cancer and its holistic approach to treatment.
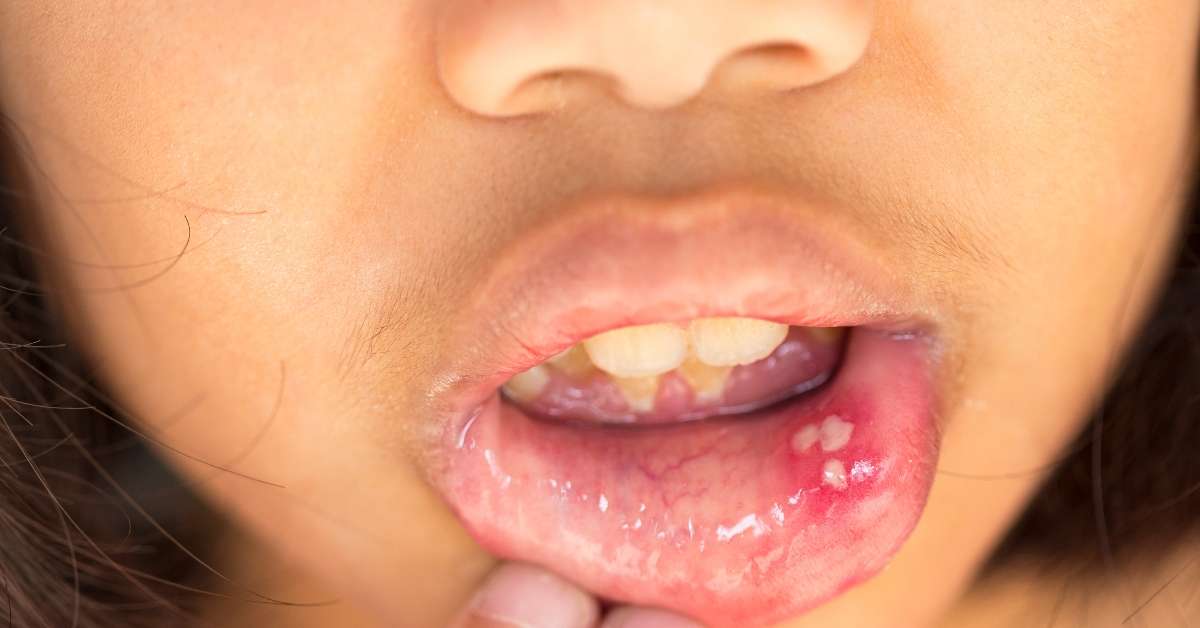
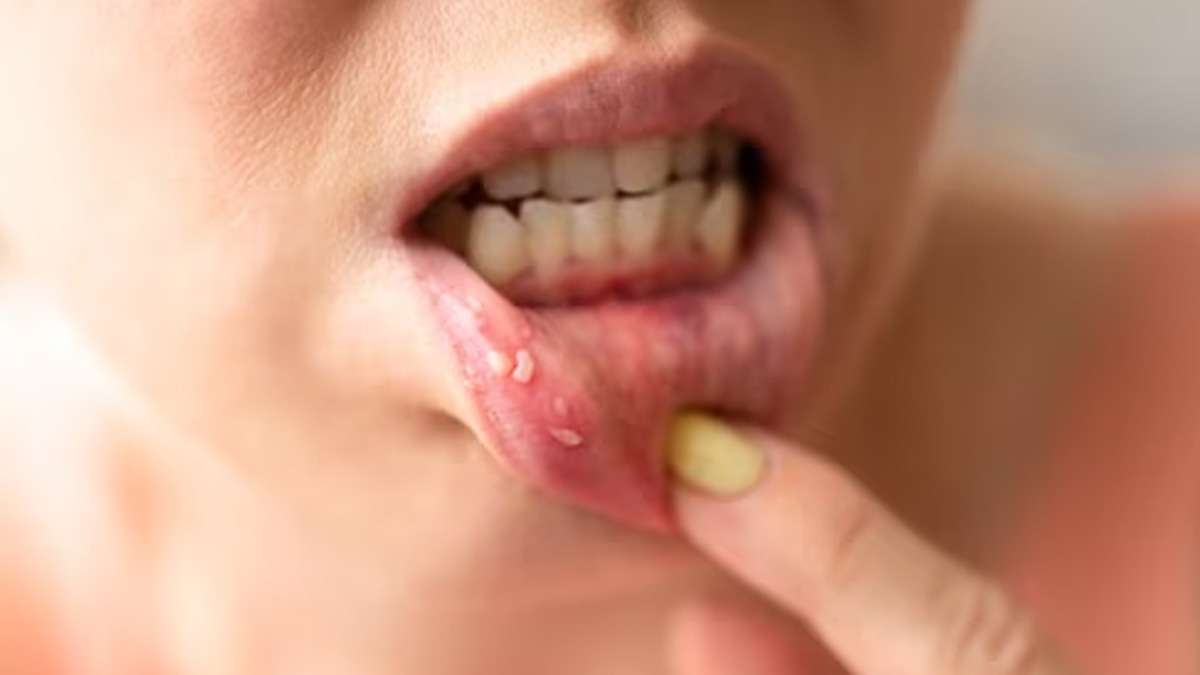
Signs and Symptoms of Mouth Cancer:
1. Persistent mouth sores: Sores that do not heal within two weeks.
2. Red or white patches: Red or white patches on the gums, tongue, tonsils, or lining of the mouth.
3. Swelling or lumps: Unexplained swelling, lumps, or thickening of the lips, gums, or other areas in the mouth.
4. Persistent pain or discomfort: Persistent pain, tenderness, or numbness in the mouth or on the tongue.
5. Difficulty in swallowing or chewing: Trouble with swallowing or chewing, or feeling like something is caught in the throat.
6. Changes in voice: Hoarseness or changes in voice quality.
7. Loose teeth or dentures: Loose teeth or ill-fitting dentures without any apparent cause.
8. Unexplained weight loss: Significant and unexplained weight loss.
Common Causes of Mouth Cancer:
1. Tobacco use: Smoking or chewing tobacco is a significant risk factor for mouth cancer.
2. Alcohol consumption: Excessive and long-term alcohol consumption increases the risk of developing oral cancer.
3. Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection: Certain strains of HPV are associated with an increased risk of mouth cancer.
4. Sun exposure: Prolonged exposure to the sun can increase the risk of lip cancer.
5. Poor oral hygiene: Neglecting oral hygiene can contribute to the development of mouth cancer.
Risk Factors for Mouth Cancer:
1. Tobacco and alcohol use: The combined use of tobacco and alcohol significantly increases the risk of developing mouth cancer.
2. Age and gender: The risk increases with age, and men are more prone to develop oral cancer than women.
3. HPV infection: Certain strains of HPV, particularly HPV16, increase the risk of mouth cancer.
4. Sun exposure: Frequent and prolonged exposure to the sun without adequate protection increases the risk of lip cancer.
5. Poor diet: A diet lacking in fruits and vegetables may contribute to an increased risk.
Diagnosis of Mouth Cancer:
Mouth cancer can be diagnosed through various methods, including:
1. Oral examination: A thorough examination of the mouth, gums, tongue, and throat by a healthcare professional.
2. Biopsy: A small sample of tissue is collected from the affected area for laboratory analysis.
3. Imaging tests: X-rays, CT scans, MRI scans, or PET scans may be performed to determine the extent and spread of cancer.
Prevention Strategies, Diet, and Lifestyle Considerations:
1. Avoid tobacco and alcohol: Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol consumption can significantly reduce the risk of mouth cancer.
2. Practice safe sex: Reducing the risk of HPV infection through safe sexual practices and HPV vaccination can lower the risk of oral cancer.
3. Protect from sun exposure: Use lip balm with SPF and wear a wide-brimmed hat to protect the lips from excessive sun exposure.
4. Maintain good oral hygiene: Brushing teeth twice a day, flossing daily, and regular dental check-ups are essential for oral health.
5. Consume a healthy diet: Include a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats in your diet.
Homoeopathic Medicine for Mouth Cancer:
Homoeopathic medicine focuses on individualized treatment based on the specific symptoms and overall health of the patient. While homoeopathy can offer supportive care, it is essential to consult a qualified homoeopathic practitioner for personalized treatment recommendations.
Conclusion:
Mouth cancer is a serious condition that requires attention and proactive management. By understanding the signs, symptoms, causes, risk factors, diagnosis methods, prevention strategies, diet and lifestyle considerations, and considering homoeopathic medicine as a complementary approach, individuals can enhance their chances of early detection and effective treatment. Remember to consult healthcare professionals for an accurate diagnosis and to create a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to your specific needs.
Leave a Message