Title: Kidney Disease: Signs, Symptoms, Causes, Risk Factors, Diagnosis, Prevention, Diet, Lifestyle, and Homoeopathic Medicine
Introduction:
Kidney disease refers to the impairment of kidney function, which can lead to various health complications if left untreated. Understanding the signs, symptoms, causes, risk factors, diagnosis methods, prevention strategies, the importance of a healthy diet and lifestyle, and the potential role of homoeopathic medicine is crucial for managing kidney disease. In this blog post, we will delve into the key aspects of kidney disease and explore how a holistic approach, including homoeopathic treatment, can contribute to overall kidney health.
Signs and Symptoms of Kidney Disease:
1. Fatigue and weakness: Feeling tired and lacking energy even with adequate rest.
2. Swelling: Edema, particularly in the hands, feet, or face.
3. Changes in urine: Foamy or bubbly urine, frequent urination, dark urine, or blood in the urine.
4. High blood pressure: Uncontrolled or persistent hypertension.
5. Loss of appetite: Decreased desire to eat and unintended weight loss.
6. Sleep problems: Difficulty sleeping due to muscle cramps or restless legs syndrome.
7. Changes in skin: Dry and itchy skin or skin discoloration.
8. Nausea and vomiting: Feeling nauseous and experiencing episodes of vomiting.
Common Causes of Kidney Disease:
1. Diabetes: Uncontrolled diabetes can damage the blood vessels and filtering units of the kidneys.
2. High blood pressure: Prolonged hypertension can strain the kidneys, leading to kidney damage.
3. Glomerulonephritis: Inflammation of the kidney's filtering units (glomeruli).
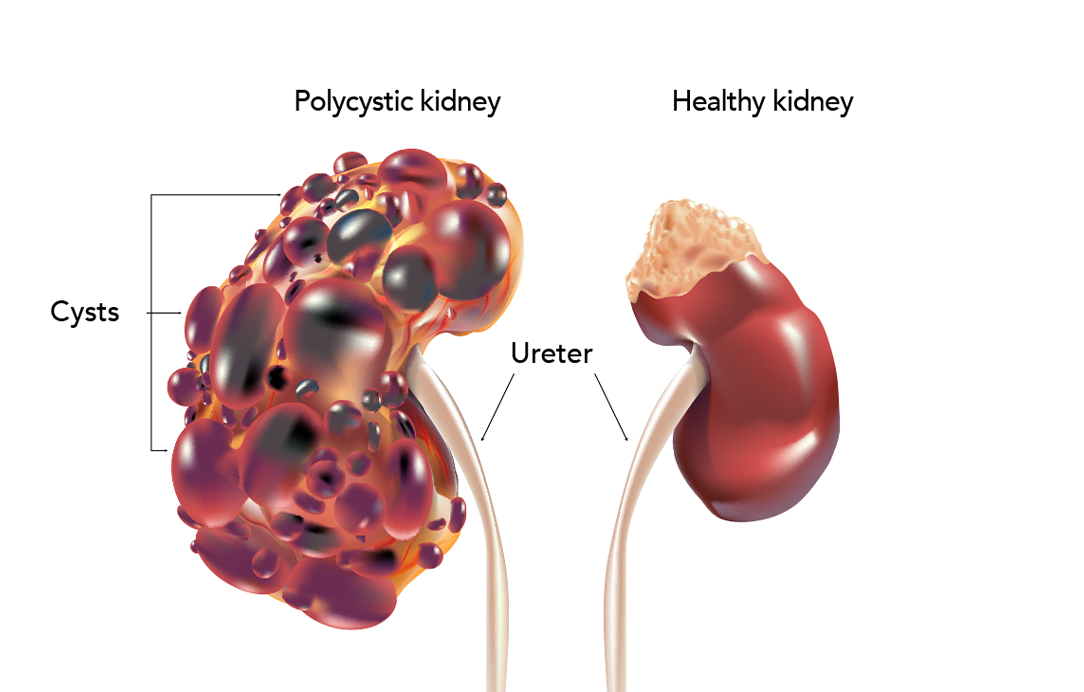
4. Polycystic kidney disease: Inherited condition where cysts develop in the kidneys, impacting their function.
5. Urinary tract obstructions: Conditions such as kidney stones or tumors can obstruct urine flow and cause kidney damage.
6. Certain medications: Long-term use of certain medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or certain antibiotics, can harm the kidneys.
Risk Factors for Kidney Disease:
1. Diabetes or high blood pressure: These are the leading causes of kidney disease.
2. Family history: A family history of kidney disease may increase the risk.
3. Age: The risk of kidney disease increases with age.
4. Ethnicity: Certain ethnicities, such as African Americans, Hispanics, and Native Americans, have a higher risk.
5. Obesity: Excess weight can contribute to the development of kidney disease.
Diagnosis of Kidney Disease:
1. Blood tests: Measure kidney function by assessing levels of creatinine, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), and glomerular filtration rate (GFR).
2. Urine tests: Examine the urine for abnormalities, such as protein or blood.
3. Imaging tests: Ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI to visualize the kidneys and detect any structural abnormalities.
4. Kidney biopsy: A small tissue sample is taken from the kidney for analysis.
Prevention Strategies, Diet, and Lifestyle Considerations:
1. Manage underlying conditions: Control diabetes and maintain blood pressure within a healthy range.
2. Stay hydrated: Drink an adequate amount of water each day.
3. Quit smoking: Smoking can worsen kidney disease and increase the risk of complications.
4. Limit alcohol consumption: Excessive alcohol intake can harm the kidneys.
5. Exercise regularly: Engage in regular physical activity to promote overall health.
6. Maintain a healthy weight: Follow a balanced diet and manage weight to reduce the risk of kidney disease.
7. Limit salt and processed food intake: Reduce sodium consumption to support kidney health.
Dietary Recommendations for Kidney Disease:
1. Monitor protein intake: Adjust protein consumption based on individual needs and kidney function.
2. Control phosphorus and potassium: Limit foods high in phosphorus and potassium, such as processed foods, dairy products, and certain fruits and vegetables.
3. Moderate sodium intake: Limit salt intake to manage blood pressure and fluid balance.
4. Stay hydrated: Drink enough fluids to prevent dehydration, but consult a healthcare professional for personalized fluid recommendations.
Homoeopathic Medicine for Kidney Disease:
Homoeopathy offers a holistic approach to managing kidney disease. The selection of homoeopathic medicines is based on an individual's specific symptoms, overall health, and the underlying cause of kidney disease. Some commonly used homoeopathic remedies for kidney disease include:
1. Apis mellifica: Indicated for kidney inflammation, swelling, and burning urine.
2. Lycopodium clavatum: Recommended for kidney diseases associated with digestive disturbances and bloating.
3. Cantharis vesicatoria: Useful for kidney infections and severe burning during urination.
It is crucial to consult a qualified homoeopathic practitioner for an accurate diagnosis, individualized treatment plan, and proper monitoring of kidney health.
Conclusion:
Kidney disease is a serious condition that requires attention and care. By recognizing the signs, understanding the causes, managing risk factors, adopting preventive measures, following a kidney-friendly diet and lifestyle, and considering the potential benefits of homoeopathic medicine, individuals can enhance kidney health and overall well-being. Always consult healthcare professionals for an accurate diagnosis and to create a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to your specific needs.
Leave a Message